Breast Cancer Treatment
Breast Cancer Treatment
KEY POINTS
- Breast cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the breast.
- A family history of breast cancer and other factors increase the risk of breast cancer.
- Breast cancer is sometimes caused by inherited gene mutations (changes).
- The use of certain medicines and other factors decrease the risk of breast cancer.
- Signs of breast cancer include a lump or change in the breast.
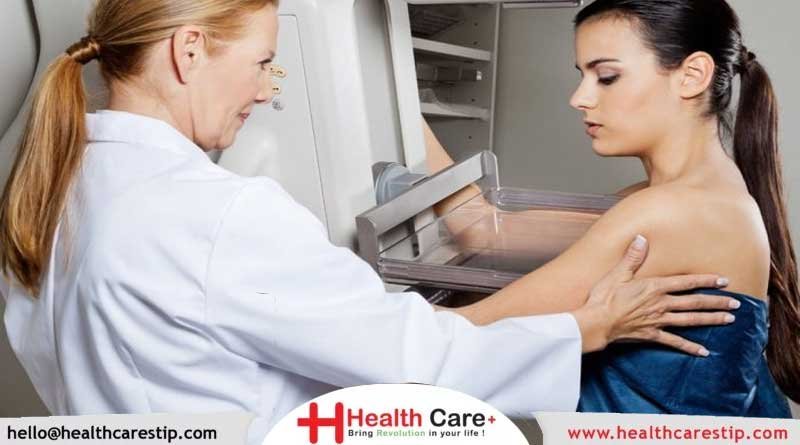
- Tests that examine the breasts are used to diagnose breast cancer.
- If cancer is found, tests are done to study the cancer cells.
- Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.
Breast cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the breast.
The bosom is comprised of curves and pipes. Each bosom has 15 to 20 areas called curves. Every curve has numerous more modest areas called lobules. Lobules end in many little bulbs that can make milk. The curves, lobules, and bulbs are connected by meager cylinders called conduits.
Each bosom likewise has veins and lymph vessels. The lymph vessels convey a practically lackluster, watery liquid called lymph. Lymph vessels convey lymph between lymph hubs. Lymph hubs are little, bean-molded structures tracked down all through the body. They channel lymph and store white platelets that assist with battling contamination and illness. Gatherings of lymph hubs are tracked down close to the bosom in the axilla (under the arm), over the collarbone, and in the chest.
The most well-known sort of bosom disease is ductal carcinoma, which starts in the cells of the conduits. Malignant growth that starts in the curves or lobules is called lobular carcinoma and is more frequently tracked down in the two bosoms than are different kinds of bosom disease. Provocative bosom malignant growth is a phenomenal kind of bosom disease where the bosom is warm, red, and enlarged.
A family background of bosom malignant growth and different elements increment the gamble of bosom disease.
Anything that builds your possibility getting a sickness is known as a gamble factor. Having a gamble factor doesn’t imply that you will get malignant growth; not having risk factors doesn’t imply that you won’t get disease. Converse with your primary care physician assuming you figure you might be in danger for bosom malignant growth.
Risk factors for bosom malignant growth incorporate the accompanying:
- An individual history of obtrusive bosom malignant growth, ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), or lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS).
- An individual history of harmless (noncancer) bosom sickness.
- A family background of bosom malignant growth in a first-degree relative (mother, girl, or sister).
- Acquired changes in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 qualities or in different qualities that increment the gamble of bosom disease.
- Bosom tissue that is thick on a mammogram.
- Openness of bosom tissue to estrogen made by the body. This might be brought about by:
Bleeding at an early age. - More seasoned age at first birth or never having conceived an offspring.
- Beginning menopause at a later age.
- Taking chemicals, for example, estrogen joined with progestin for side effects of menopause.
- Therapy with radiation treatment to the bosom/chest.
- Drinking liquor.
- Weight.
- More seasoned age is the principal risk factor for most tumors. The possibility getting disease increments as you age.
NCI’s Bosom Malignant growth Hazard Evaluation Instrument utilizes a lady’s gamble elements to gauge her gamble for bosom disease during the following five years and up to mature 90. This internet based device is intended to be utilized by a medical care supplier. For more data on bosom disease risk, call 1-800-4-Malignant growth.
SKIN | PAIN | DIABETES | CANCER | HEART ATTACK | NUTRITIONS | AVOID | HEALTHY FOOD